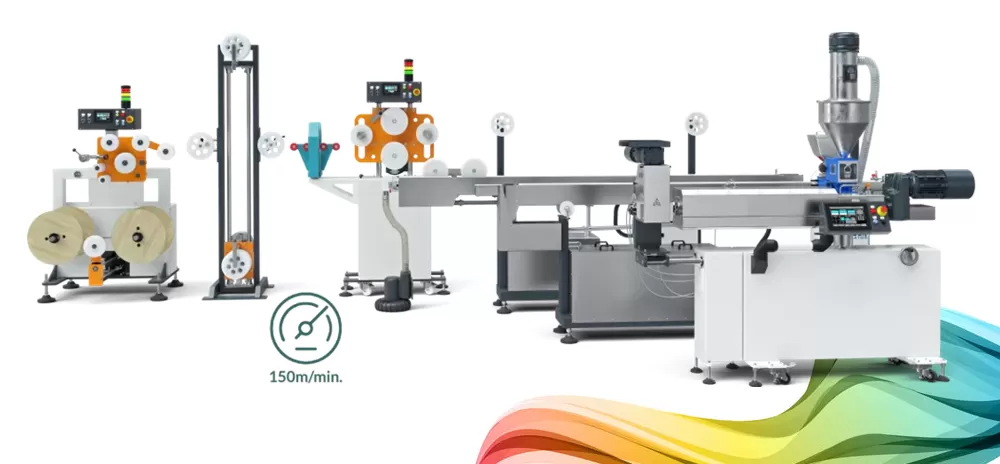
There are many different types of filaments in the world of 3D printing, the two most popular being PLA (polylactide)...

Filament Easy PLA Alien...
dashboard
clear
-
 Filament Easy PLA Candy 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Candy 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Black 1,75 mm 2,5kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Black 1,75 mm 2,5kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Blue 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Blue 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Brown 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Brown 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Burgundy 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Burgundy 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Graphite 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Graphite 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Gray 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Gray 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Green 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Green 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Inox 1.75mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Inox 1.75mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Light Green 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Light Green 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Midnight Sky 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Midnight Sky 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Navy Blue 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Navy Blue 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Old Gold 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Old Gold 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA ONYX 1,75 mm 0,85 kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA ONYX 1,75 mm 0,85 kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Orange 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Orange 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Pastel Blue 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Pastel Blue 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Pastel Lilac 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Pastel Lilac 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Pastel Mint 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Pastel Mint 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Pastel Yellow 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Pastel Yellow 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Pink 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Pink 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Red 1,75 mm 0,85 kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Red 1,75 mm 0,85 kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Red Orange 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Red Orange 1.75 mm 0.85 kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Ruby Red 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Ruby Red 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Spectra Blue 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Spectra Blue 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA True Blue 1,75 mm 0,85 kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA True Blue 1,75 mm 0,85 kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA True Gold 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA True Gold 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA White 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA White 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
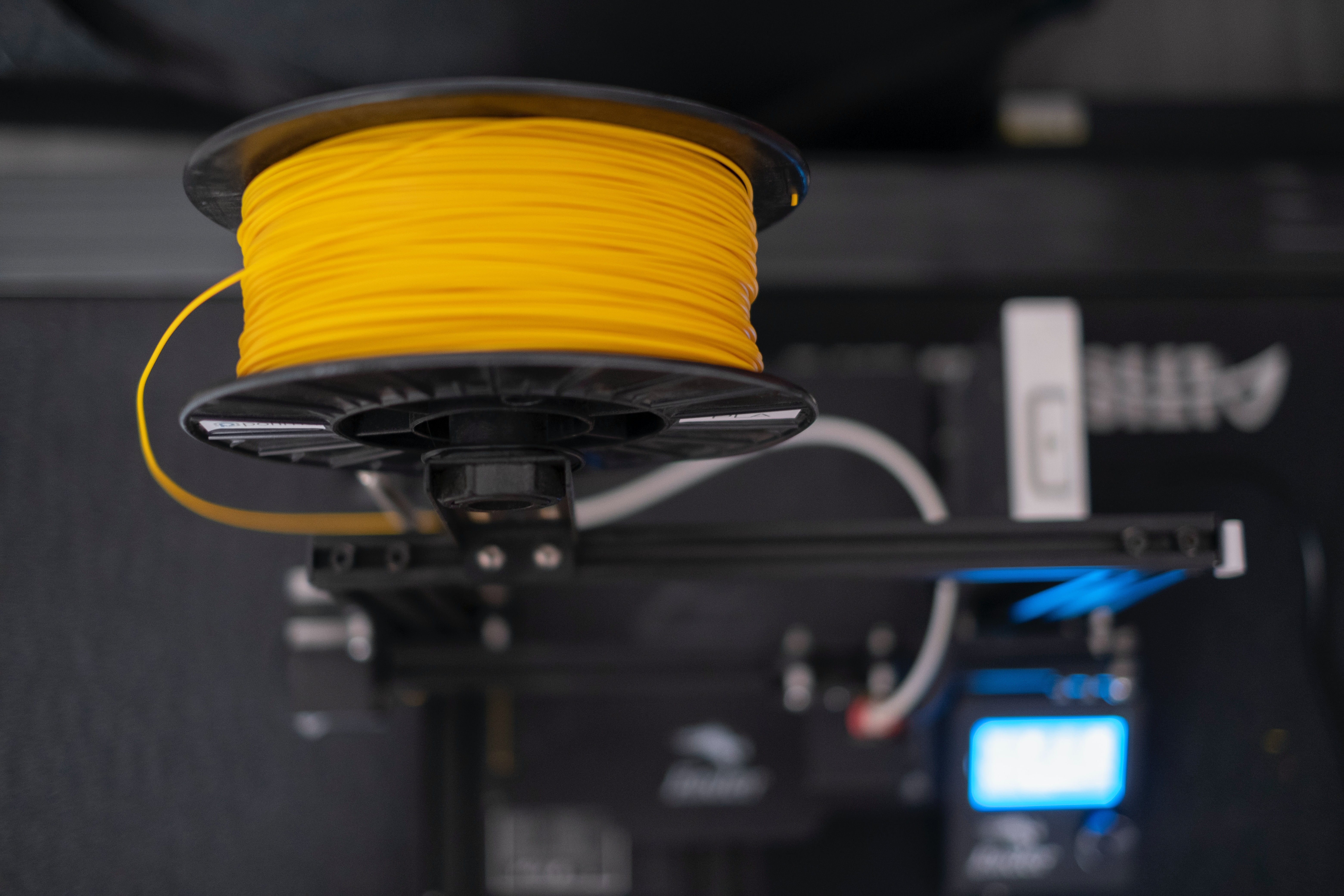
 Filament Easy PLA Yellow 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Yellow 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Aurora 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Aurora 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Beige 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Beige 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Vertigo 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Vertigo 1.75 mm 0.85kg Fiberlogy -
 Filament Easy PLA Black 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
Filament Easy PLA Black 1,75 mm 0,85kg Fiberlogy
zł88.40
zł104.00
-15%
- -15%

























































Zostaw komentarz